Loading advertisement...
27-02-2025

The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Exam 2025 was conducted on February 27, 2025, from 10:30 AM to 1:30 PM. With lakhs of students appearing for the exam, the difficulty level, tricky questions, and time management became hot topics of discussion.
Now, as students eagerly wait for results, unofficial answer keys from various coaching institutes help them analyze their performance. This blog covers set-wise answer keys, student reactions, and expert analysis.
After exiting the exam hall, students had mixed reactions. Some found the paper balanced and NCERT-based, while others struggled with tricky numericals and conceptual questions.
🔹 "The paper was easier than expected!" – Many students felt the exam was moderate in difficulty, with direct NCERT-based questions in Physical and Organic Chemistry.
🔹"Numericals were a bit tricky." – Some students mentioned that mole concept and electrochemistry numericals required deep thinking but were solvable.
🔹"Inorganic Chemistry was tough!" – Many found questions from p-block and coordination compounds tricky, requiring strong conceptual clarity.
🔹"Time management was key!" – The paper was considered lengthy, with section C and D consuming most of the time. Students who practiced well managed to complete it on time.
🔹 "Case-study questions were easy." – The competency-based case study questions were considered simple by most students.
🔹"Assertion-Reason questions were confusing." – Some assertion-reason questions were tricky and needed deep conceptual understanding.
Check: CBSE Class 12th Physics Answer Key
Experts from leading coaching institutes reviewed the paper and shared the following insights:
🔹 Overall Difficulty Level: Moderate – Neither too easy nor too difficult.
🔹 Physical Chemistry: Moderate – Numericals were solvable but required proper formulas.
🔹 Organic Chemistry: Easy to Moderate – Mostly NCERT-based, but a few tricky conversions.
🔹 Inorganic Chemistry: Difficult – Some conceptual questions were confusing.
🔹 Case Study Questions: Easy – Straightforward and scoring.
🔹 Assertion-Reasoning Questions: Moderate to Difficult – Some were tricky and required deep knowledge.
👉 Verdict: Students who studied NCERT thoroughly and practiced previous years’ papers could score well.
| Question set | Link |
|---|---|
| Set -1 (56/2/1) | Click Here |
| Set -2 (56/2/2) | Click Here |
| Set -3 (56/2/3) | Click Here |
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer key
Set 1- (56/2/1)
SECTION - A
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The charge required for the reduction of 1 mol of MnO4−to MnO2 is (A) 1 F (B) 3 F (C) 5 F (D) 6 F | (B) 3 F |
| 2. Which among the following is a false statement? (A) Rate of zero-order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant. (B) Half-life of a zero-order reaction is inversely proportional to the rate constant. (C) Molecularity of a reaction may be zero. (D) For a first-order reaction, t1/2= 0.693/k. | (C) Molecularity of a reaction may be zero. |
| 3. The number of molecules that react with each other in an elementary reaction is a measure of the (A) the activation energy of the reaction (B) stoichiometry of the reaction (C) the molecularity of the reaction (D) order of the reaction | (C) molecularity of the reaction |
| 4. The element having [Ar]3d104s2 electronic configuration is (A) Cu (B) Zn (C) Cr (D) Mn | (B) Zn |
| 5. The complex ions [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+and [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]2+ are called (A) Ionization isomers (B) Linkage isomers (C) Co-ordination isomers (D) Geometrical isomers | (B) Linkage isomers |
| 6. The diamagnetic species is: (A) [Ni(CN)4]2- (B) [NiCl4]2− (C) [Fe(CN)6]3− (D) [CoF6]3− | (A) [Ni(CN)4]2- |
7. Which is the correct IUPAC name for the given compound? 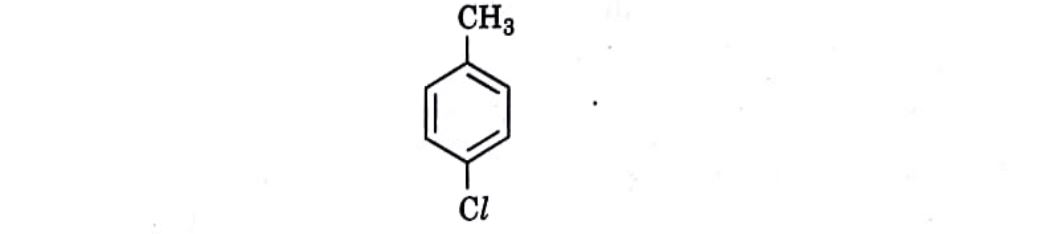 (A) Methylchlorobenzene | (C) 1-Chloro-4-Methylbenzene |
| 8. What will be formed after the oxidation reaction of secondary alcohol with chromic anhydride (CrO3)? (A) Aldehyde (B) Ketone (C) Carboxylic acid (D) Ester | (B) Ketone |
| 9. The conversion of phenol to salicylic acid can be accomplished by (A) Reimer-Tiemann reaction (B) Friedel-Crafts reaction (C) Kolbe reaction (D) Coupling reaction | (A) Reimer-Tiemann reaction |
| 10. Which of the following is/are examples of denaturation of protein? (A) Coagulation of egg white (B) Curdling of milk (C) Clotting of blood (D) Both (A) and (B) | (D) Both (A) and (B) |
| 11. Nucleotides are joined together by (A) Glycosidic linkage (B) Peptide linkage (C) Hydrogen bonding (D) Phosphodiester linkage | (D) Phosphodiester linkage |
| 12. Scurvy is caused due to deficiency of (A) Vitamin B1 (B) Vitamin B2 (C) Ascorbic acid (D) Glutamic acid | (C) Ascorbic acid |
For questions numbers 13 to 16, two statements are given – one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C), and (D) as given below: (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). 13. Assertion (A): In a first-order reaction, if the concentration of the reactant is doubled, its half-life is also doubled. | (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. |
14. Assertion (A): Cu cannot liberate H2 in reaction with dilute mineral acids. | (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). |
15. Assertion (A): Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis. | (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). |
16. Assertion (A): Vitamin D cannot be stored in our body. | (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. |
We will be updating the more answers soon...